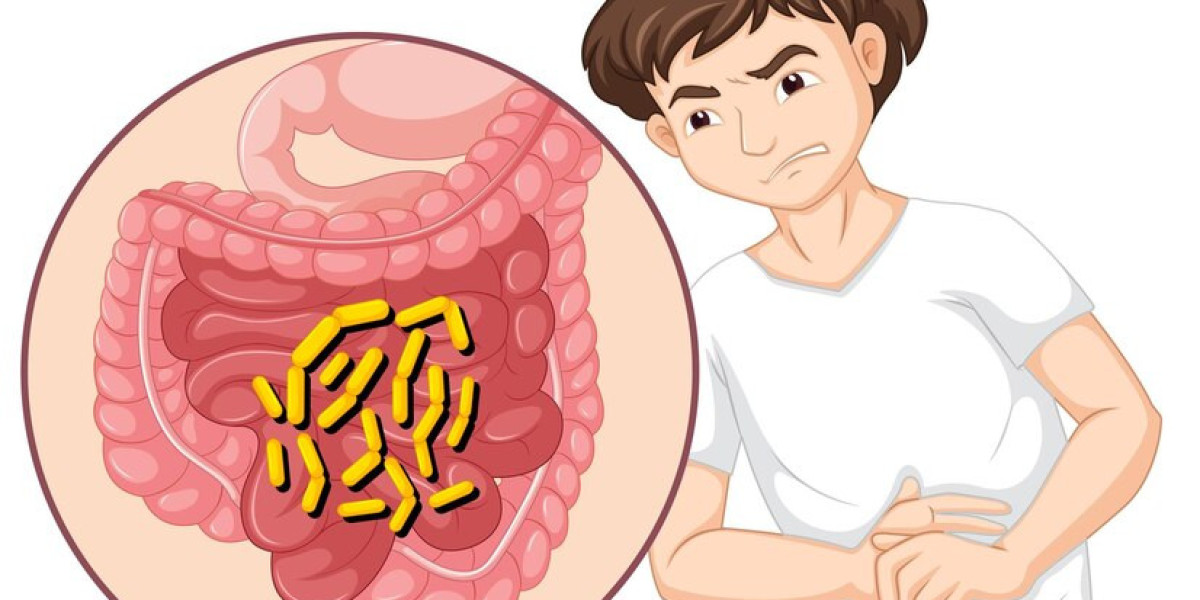
Fenbendazole is a well-known anthelmintic medication widely used in veterinary medicine to treat parasitic worm infections, especially in animals such as dogs, cats, livestock, and horses. Because of its broad use and reputation for safety, many people wonder whether Fenbendazole is effective against all parasites.
What Is Fenbendazole?
Fenbendazole 444Mg belongs to the benzimidazole class of antiparasitic drugs. It works by disrupting the parasite’s ability to absorb glucose, which leads to energy depletion and eventual death of the parasite. The drug is particularly effective against many gastrointestinal worms, making it a mainstay treatment in veterinary parasitic control programs.
Parasites Fenbendazole Is Effective Against
Fenbendazole has a broad spectrum of activity against several intestinal helminths (worms). These include:
Roundworms (nematodes) such as Toxocara and Ascaris
Hookworms like Ancylostoma species
Whipworms (Trichuris species)
Certain lungworms in animals
Some tapeworms, particularly Taenia species
Because of this wide coverage, Fenbendazole is commonly used as a first-line dewormer for dogs, cats, and farm animals. It is especially valued for its ability to target multiple worm species with a relatively low risk of side effects.
Protozoan parasites: Fenbendazole does not reliably treat protozoa such as Giardia, Entamoeba, Plasmodium (malaria), or Toxoplasma. While it may show limited activity against Giardia in some animals, it is not considered a definitive or standalone treatment.
Flukes (trematodes): Parasites like liver flukes (Fasciola hepatica) are not effectively treated with Fenbendazole. Drugs such as Triclabendazole are specifically required for these infections.
Certain tapeworms: Fenbendazole is ineffective against Echinococcus species and some other tapeworms, which require medications like Praziquantel.
External parasites: Fleas, ticks, mites, and lice are not affected by Fenbendazole, as it only works on internal parasites.
Parasites vary greatly in their biology and metabolism. Fenbendazole targets microtubule formation and glucose uptake, mechanisms that are crucial for many worms but not universal across all parasite groups. Protozoa and flukes have different cellular structures and metabolic pathways, making them resistant to Fenbendazole’s mode of action. This is why parasite identification is critical before selecting a treatment. Buy Fenbendazole 444 Mg Online at best pharmacy Medzsupplier.
Resistance and Effectiveness
Another factor affecting Fenbendazole’s effectiveness is drug resistance, especially in livestock. Over time, repeated or improper use can lead to reduced sensitivity in certain worm populations. This does not mean Fenbendazole is ineffective, but it highlights the importance of correct dosing, treatment duration, and rotation with other anthelmintics when necessary.
Use in Humans: A Cautionary Note
Fenbendazole is primarily approved for veterinary use. While there is growing public interest in its off-label applications, human use should only occur under strict medical supervision, if at all. Other medications such as Albendazole, Mebendazole, or Praziquantel are better studied and approved for human parasitic infections.
Conclusion
Fenbendazole is a highly effective antiparasitic drug, but it is not a universal solution for all parasites. It works best against a wide range of intestinal worms, including roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, and some tapeworms. However, it does not treat protozoa, flukes, many tapeworm species, or external parasites. For complete parasite control, accurate diagnosis and parasite-specific treatment are essential. Fenbendazole remains a valuable tool in parasite management—but only when used for the right parasites and in the right context.